 Copy Lattice CPLD Encrypted File
Copy Lattice CPLD Encrypted File
Copy Lattice CPLD Encrypted File from embedded memory, disable the security fuse by Microcontroller cracking skill and extract the firmware from CPLD chip;
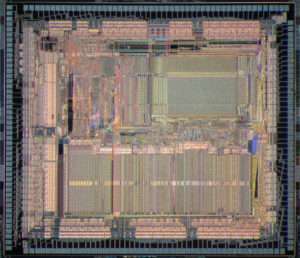
Copy Lattice CPLD Encrypted File from embedded memory, disable the security fuse by Microcontroller cracking skill and extract the firmware from CPLD chip;
Normally a microscope objective has at least two parameters printed on it – magnification and numerical aperture (NA). Modern optical microscopes provide magnification up to 9,000× and 500× magnification is provided by most modern microscopes. Numerical aperture determines the resolving power of an objective, but the total resolution of a microscope system is also dependent upon the numerical aperture of projection optics.
The higher the numerical aperture of the total system the better the resolution. The numerical aperture is related to the angle µ which is one-half of the angular aperture at which the light cone comes to the specimen surface: NA = n sin(µ). The relationship between the numerical aperture and the resolution can used for observation.