 Copy Microcontroller PIC16F639 Heximal
Copy Microcontroller PIC16F639 Heximal
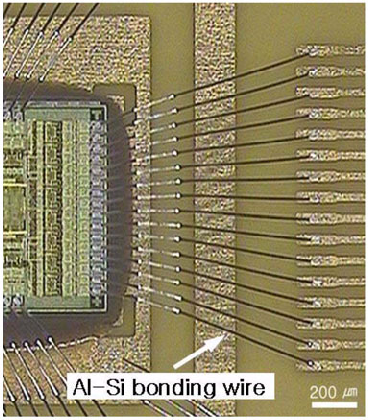
Copy Microcontroller PIC16F639 Heximal needs to extract the flash program from microprocessor PIC16F639 and then crack microcontroller pic16f639 security fuse bit;
A single comparator is shown in Figure 6-1, along with the relationship between the analog input levels and the digital output. When the analog input at VIN+ is less than the analog input VIN-, the output of the comparator is a digital low level. When the analog input at VIN+ is greater than the analog input VIN-, the output of the comparator is a digital high level. The shaded areas of the output of the comparator in Figure 6-1 represent the uncertainty due to input offsets and response time.
The polarity of the comparator output can be inverted by setting the CINV bit (CMCON<4>). Clearing CINV results in a non-inverted output. A complete table showing the output state versus input conditions and VIN-the polarity bit.
There are eight modes of operation for the comparator. The CMCON register, shown in Register 6-1, is used to select the mode. Figure 6-2 shows the eight possible modes. The TRISA register controls the data direction of the comparator pins for each mode.
If the Comparator mode is changed, the comparator output
The CMCON register, shown in Register 6-1, is used to select the mode. Figure 6-2 shows the eight possible modes. The TRISA register controls the data direction of the comparator pins for each mode.
A simplified circuit for an analog input is shown in Figure 6-3. Since the analog pins are connected to a digital output, they have reverse biased diodes to VDD and VSS. The analog input, therefore, must be between VSS and VDD. If the input voltage deviates from this libri the polarity bit.
Response time is the minimum time, after selecting a new reference voltage or input source, before the comparator output is ensured to have a valid level. If the internal reference is changed, the maximum delay of the internal voltage reference must be considered when using the comparator outputs. Otherwise, the maximum delay of the comparators should be used H-CN;