Posts Tagged ‘cypress ic flash break’
 IC Flash Recovery
IC Flash Recovery
IC Flash Recovery is a process to extract code of MCU memory content, and copy the firmware to new Microcontroller for IC cloning;
IC Flash Recovery is a process to extract code of MCU memory content, and copy the firmware to new Microcontroller for IC cloning
Semi-invasive IC Flash Recovery, like invasive ic attack, require depackaging the chip to get access to the chip surface. But the passivation layer of the chip remains intact – semi-invasive ic break methods do not require electrical contact to the metal surface, so there is no mechanical damage to the silicon.
As invasive ic hacks are becoming constantly more demanding and expensive, with shrinking feature sizes and increasing device complexity, semi-invasive ic flash recovery become more attractive as they do not require very expensive tools and give results in a shorter time. Also, being applied to a whole transistor or even a group of transistors they are less critical to the small feature size of modern chips.
 Break IC Flash
Break IC Flash
Break IC flash could be also applied to the device communication protocol in order to find any hidden functions embedded by the software developer for testing and upgrade purposes.
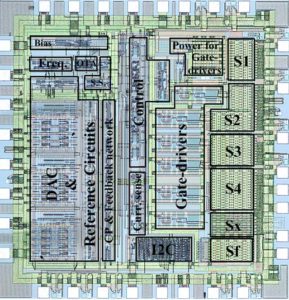
Break IC flash could be also applied to the device communication protocol in order to find any hidden functions embedded by the software developer for testing and upgrade purposes
IC Chip manufacturers very often embed hardware test interfaces for postproduction testing of their semiconductor devices. If the security protection for these interfaces is not properly designed, the ic attacker can exploit it to get access to the on-chip memory. In smartcards such test interfaces are normally located outside the chip circuit and physically removed after the test operation, eliminating any possibility of use by outsiders.
Any security system, either software or hardware, could also have holes in its design and there is always a small chance that an ic cloner would eventually find one with brute force random testing. Careful design of the security protection, followed by proper evaluation, could help avoid many problems and make such MCU attack virtually impossible.